
Referential and Reviewed International Scientific-Analytical Journal of Ivane Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University, Faculty of Economics and Business

Inclusive Growth-The Qualitative Innovation of Georgian Social and Economic Development Strategy
Econonmic growth is an important challenge for every country, especially for developing ones, including Georgia. Actually, economics of Georgia was increased without significant growth of the number of employed. As a response of this challenge in 2014 the Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgia – Georgia 2020 was published aiming identification of key problems and challenges preventing development of the foundation for a long-term inclusive economic growth and improvement of welfare of the population.
The social and economic development program/strategy of Georgia - “Georgia 2020”- is relevant to the world trends, Georgia is relevant to world trends, as the main goal of the strategy is identification of the preventive factors of inclusive economic growth and defining the social-economic policy for overcoming it.
Inclusive economic growth was the main direction of country economic development, the result is long-term nature based on the strategy complexity and its activities after 2020, but the information about certain activities implemented by Government of Georgia and the achieved results is not known for the society. Activities made in the field of entrepreneurship, starting from Estonian model of income, finished with simplified business administration, are very positive and correct step, especially in the field of strengthening small and medium enterprise.
The thesis focuses on inclusive growth model as a main qualitative innovation of Georgian social and economic development strategy- Georgia 2020 and the conditions of its achievement, on the long-term oriented actions for achievement of the mentioned results ad compliance to the goals of the strategy.
We consider that for an effective result the state shall pay the special attention to the components included state strategy on education quality essurance, employment of the population of all the level and development of real production. Also, it is important that each specific step was more detailed oriented or oriented on the results for inclusive growth, as only economic growth does not bring automatic improvement of poor’s conditions. Though sustainable economic growth will be a strong basis for further inclusive growth and improvement of the condition of poors.
Keywords: Economic growth, inclusive growth, equality.
JEL Codes: O10, O11, O12
Georgian Economics was in hard situation after restoration of state independence, the main challenge, development of market economy was the key challenge for the under-developed state institutions. During 28 years of state independent, in addition to challenge the state faced several internal confrontation or military action, what impacted significantly the territorial integrity of the country and accordingly the economy of Georgia. Positive changes in the state economy, especially in the direction of investments has started since 2005 (Diagram N1).
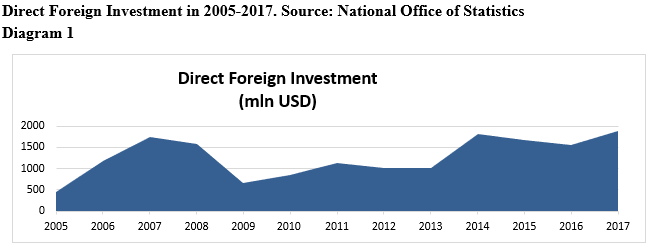
It made economic development in combination with the series of in-depth transformation faster in the country. Russian Georgian war of 2008 was one of the important obstacles in this directon. The external shock supporting to increased risk for investors dramatically reduced the number of investments in Georgia (National Service of Statistics).
It is important, that in addition to the important external factors, in certain cases the steps made from the side of the state was not adequate to the formalized development visions. For that period, Georgia, positioning of Georgia as the Singapore was an official declared approach of the government, when Georgia is not able and cannot share neither by geographic resource, nor by state regulating direction the economic politics implemented by Singapore for achievement economic miracle. As the role of the state was and is great in the economic processes… including protection of labour market, in the certain segments of the market by appliance of protectionist norms, ( Khaduri 2018, 50), from the prospective of regulating, especially labour market regulation, compared to Georgian condition, in 2006 labour inspection was totally cancelled, what brought us to the difficult challenges available in Georgia (Kenchoshvili 2018, 244)
Despite of this in 2003-2012 economic situation of the state was drastically changed into positive (Diagram N 2).
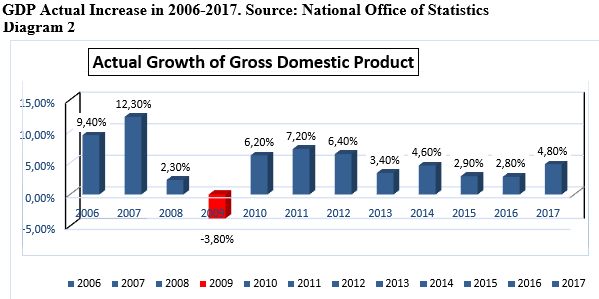
During that period the experience of Georgia ensured us once again that it is possible to make positive changes by means of autoritarian methods in economics, though for long-term economic development, it is important that democratic institutes work effectively, respect to private human freedom and high civic political culture (Beridze 2018, 35).
Regardless quite a high speed of economic growth, the situation was not improved in terms of unemployment and elimination of the poverty (Diagram 3,4).
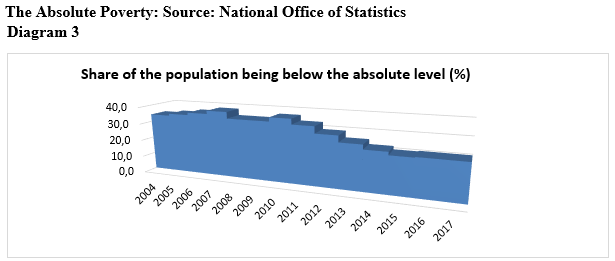
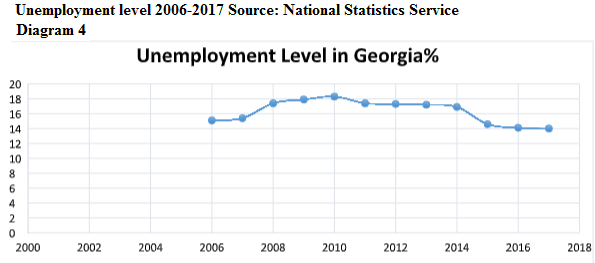
Similar to overcoming of income unequality, Gini coefficient in Georgia in 2014-2017 the gross income is increased from 0.40 to 0.41, while total monetary expenses was not changed and it is still 0.47, what makes Georgia in a difficult conditions by distribution of the income among thecountries being in poor condition, while from the regional prospective the most difficult condition is in Shida Kartli, Mtskheta-Mtianeti and Kakheti (blue line.) (Georgian Foundation For Strategic And International Studies 2017,41)
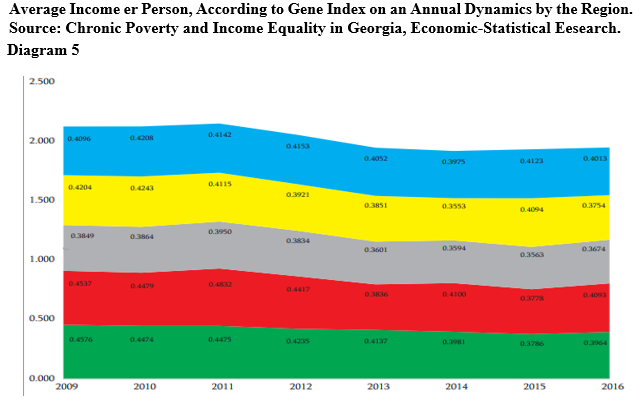
It appears that there is insignificant growth of employed in the country, the share of the people being below absolute level of poverty against total amount of the population was more reduced. Actually, economics of Georgia was increased without significant growth of the number of employed. As a response of this challenge in 2014 the Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgia – Georgia 2020 was published aiming identification of key problems and challenges preventing development of the foundation for a long-term inclusive economic growth and improvement of welfare of the population (Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgia 2020). The paper demonstrates the view of the author, about key challenges of the Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgiaand overcoming ways.
Key Challenges of the Social and Economic Development
Strategy of Georgia – Georgia 2020
According to the statistics no crucial changes are noticed for reduction of poverty, unemployment and unequality of income in Georgia since 2014. This is why it is more appropriate to investigate its reasons in the strategy and its implementation.
An inclusive economic growth is explained in the social and economic development strategy of Georgia as comprehensive inclusion of the population in economic development process and the government aims to introduce the model when in parallel to economic growth, the equal access to the economic opportunities is increasing, unemployment and poverty are reducing with support of the strategy.
Despite there is no common, unified explanation of an inclusive growth, the final goal in case of any explanation is identical. According to the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), inclusive growth is an economic growth where the opportunities are distributed fairly and accessible for everybody in the society (OECD, inclusive growth). Though the best explanation of the inclusive growth is offered by the UN Development Program, the director of sustainable development goals fund and leading economist of UN, Paloma Duran, according to her (Duran,2015), growth is inclusive, when
- Economic growth takes place in the sectors, where mainly poor people are employed.
- Economic growth takes place where mainly poor people live, even by the little resource potential;
- Such production factors are applied which are owned by the poor people, like un-skilled labour;
- The prices on such commodities are reduced which are used by poor people
Noteworthy, that inclusive economic growth and inclusive development is the actual challenge of modern economics, as inequality in the World is increasing in all the directions. For instance if in 1980 1% of population with the highest income received only 12% of national income, in 2016 more than 20% of the population gets it. In case of the Western Europe, such inequality of income is increased from 10 to 12% during 1980-2016. In 2016 50% US population with the lowest income received only 13% of Total national income, while the same stratum received 20.3% in 1980. The situation is better in the western Europe, though the level of unequality of income is comparatively better, thought it is still higher, as in 2016 50% of the population having the lowest income received 23.8% of total national income, while this data in 1980 was only 22% (9). For responding the challenge many influential economic institutes came together. EBRD developed an Economic Inclusiveness Strategy 2017-2021 for responding the changes in this direction (Economic Inclusion Strategy 2017-2021), while for the last years the World Economic Forum publishes the inclusive development index according to the countries. Based on the results of 2017, according to the report of 2018 Georgia is the 32th place in the inclusive development (World Economic Forum , 2018).
The experience of Georgia, as well as many other countries proves that even high level of growth does not ensures automatic overcoming of poverty, inequality or unemployment.
The social and economic development program/strategy of Georgia, Georgia 2020, is relevant to the world trends, Georgia is relevant to world trends, as the main goal of the strategy is identification of the preventive factors of inclusive economic growth and defining the social-economic policy for overcoming it. As a result, there are 3 key problems among the critical problems – low competitiveness of the private sector, non-relevant developed human resurce and limited access to the financial resources. (Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgia 2020, 16).
The strategy was a new approach for Georgia being combination of economic growth and economic development strategy, as fast economic growth is still the priority of the country, thoughit was written in the strategy that its goal was inclusion of every citizen in economic processes, which brings to the root and qualitative problem of the economics and series of activities for social-economic politics was developed in order to overcome it. Inclusive economic growth was the main direction of country economic development, the result is long-term nature based on the strategy complexity and its activities after 2020.
It is important to notice in order to assess program/strategy efficiency, it will not be relevant to assess the current one which was developed in 2014 and it is only 4 years since it has been developed, in order to achieve the results. Though it is important to focus together with achieved results, as well as the activities focused on the activities oriented on achievement of long-term goals and their relevance to the goals of strategy.
Currently, the information about certain activities implemented by Government of Georgia and the achieved results is not known for the society. Activities made in the field of entrepreneurship, starting from Estonian model of income, finished with simplified business administration, are very positive and correct step, especially in the field of strengthening small and medium enterprise. As it is given in the development strategy 2016-2020, small and medium business development is considered as the key direction of country economic development (The Development Strategy for Small and Medium Entrepreneurship in Georgia 2016, 4). Though talking on efficiency and accountability is fine, as state is accountable to report to the society about efficiency of the policy.
For this purpose, let’s discuss 3 main problems selected randomly to analyze. Let’s discuss one of them, the steps made for overcoming law competitiveness of private sector in the country, state support for entrepreneurship development. Noteworthy, that till 2017 state politics was implemented by different state structure, accordingly, it is very unclear what the total amount of budget for supporting entrepreneurship and specifically what the result for Georgia economy are.
Since 2017 LELP „Produce in Georgia” implements comprehensive approach independently for development of entrepreneurial environment and private sector, support of expert and attracting of investments.
The agency is actively involved in development of entrepreneurial environment and private secotor, the agency is actively participating in strengthening of local business under which the support programs in the field of industry, hotel industry, micro and small entrepreneurs.
By the data of February 01, 2019 since 2014/5, 313 projects supporting micro and small entrepreneurs were implemented, 39 583 722 GEL is issued by the state in the form of grants while total cost of investments was 49.5 million GEL (Produce in Georgia, 2019). It means that every GEL issued from the budget brought 0.25 GEL of investment. In addition, it is not clear the number of working places created by the program.
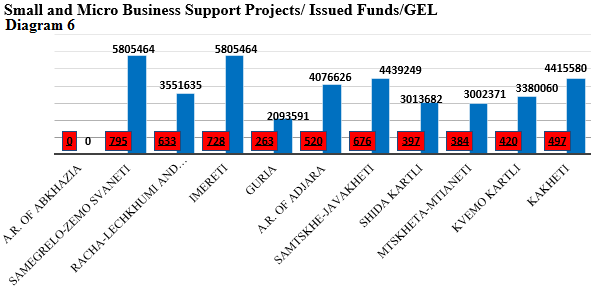
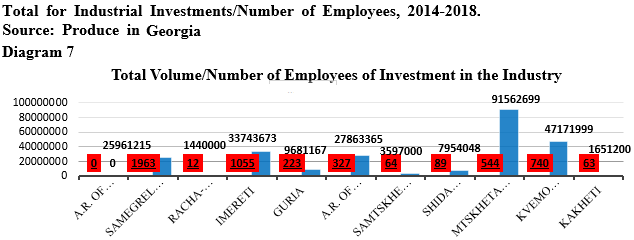
In 2014-2018 104 projects were implemented in the field of industry, total amount of investment was 250, 626, 366 GEL, which created 5,080 working place according to the agencies. In the field of the industry, new enterprises are established, as well as renovation of already operating enterprises, the agency supports already existing and potential new entrepreneurs in cooperation with commercial banks, leasing companies and informational consultations organizations. The most problematic issue is how many employment places are operational and what is the result of above mentioned direction is still unclear.
In 2019 The Minister of Economics and Sustainable Development of Georgia introduced the results of the efficiency of technical support and financial access of the industrial part (The Ministry of Economics and Sustainable Development of Georgia 2019), based on which the project results were assessed positively. Though as the research was small scaled, we think that the results are not relevant for all the aspects of the agency operation.
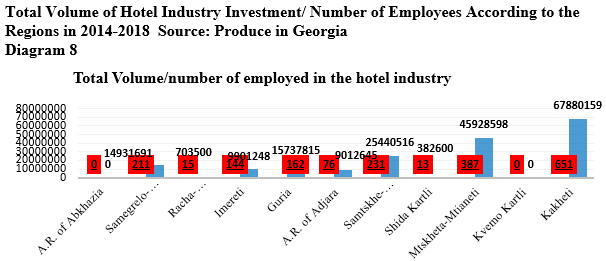
As for hotel industry except Batumi and Tbilisi, 82 projects were implemented in different regions of Georgia in 2014-2018 with total investment, 189 918 772 GEL and gained 1890 place similar to industrial direction, current situation is unknown in this direction too. Though according to the statistics of Produce in Georgia, establishment of one working place in the hotel industry required 100, 486 GEL.
In addition, the agency implements different activities supporting export and encouraging investments, though in this direction the results are not relevant in terms of calculation, accordingly, neither budget expenses spent for their implmentation, nor its efficiency can be discussed now.
Based on above mentioned it is clear that one of the important and praiseworthy programs of Georgian government has many gaps to be filled and it requires understanding of importance of transparency and accountability of the government to population. Noteworthy, like other cases that the program has a direct impact on the poor population and the program cannot be considered as improvement of inclusion component as applying the program means having certain skills (internet literacy, searching the information about the program) which is not relevant for the economically vulnerable population.
In addition to the critical thinking it is not possible to assess the reform of healthcare positively, access to general healthcare to all social stratum, directly influencing condition of the poverty and has a significant impact and the expenses of the medical services were actually reduced.
When will improvement of inclusive economic growth has a real result? Is elaboration of a long-term state policy an effective way of overcoming inequality ensuring active inclusion of poor? Or the universal way of inequality goes on correction with direct investment?
For ensuring inclusive growth in the country, there is no common, universal approach and requires consideration of all country contexts, for ensuring inclusive growth together with sustainable economic growth, it is important to develop the directions of real and result-oriented politics, such as productive employment and job places, economic transformation, investment in human resource, progressive fiscal politics, social protection, non-discriminated approach, strong institutes, etc. (15.6). In addition, it is important to consider that inclusive growth is not reached in 5 or 10 years. It is necessary to implement consequential, real and effective politics in above mentioned direction, though it does not release state from the obligation, which will be based on real needs. Active operation of municipal government in this direction is very important and coordination with the central government, as without decentralization it will be hard to bring real needs and condition to central government.
References:
- Beridze M. The Most Important Factor Inclusive - Economic Growth and Development, journ. “economica da biznesi”, N1, 2017 (In Georgian);
- Beridze T. Mekvabishvili E. (2018) “Hard Road” of Economic Reforms in Post-Communist Georgia: Retrospectives and Perspectives. Journ. “Economisti”, №1, p. 18-36 (In Georgian);
- Economic Inclusion Strategy 2017-2021. European Bank For Reconstruction And Development https://www.ebrd.com/what-we-do/projects-and-sectors/economic-inclusion.htm Last visit 07.05.2019/
- georgian foundation for strategic and international studies. Chronica Poverty and Income Equality in Georgia, Economic-Statistical Research, Tbilisi 2017, p. 41;
- https://library.fes.de/pdf-files/bueros/georgien/13977.pdf Last visit 07.05.2019|
- Inclusive Growth and Development Report 2018. Word Economic Forum http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Forum_IncGrwth_2018.pdf |Last visit 07.05.2019|
- Kenchoshvili M. (2018) For Understanding of Challenges of Georgian Labour Market.: Globalizacia da Biznesi №6, p. 242-246 (in Georgian);
- Khaduri N. (2018) Economic Development Model of Georgia and Global Economics in Post Crisis Period, „Globalizacia da Biznesi“, N6 p. 48-53 (in Georgian);
- LEPL Produce in Georgia http://www.enterprisegeorgia.gov.ge/ka /Last visit 07.05.2019|
- National Service of Statisticshttp//|www.geostat.ge/ Last visit 07.05.2019|;
- Social and Economic Development Strategy of Georgia, Georgia 2020;
- The Development Strategy for Small and Medium Entrepreneurship in Georgia, 2016-2020;
- The Ministry of Economics and Sustainable Development of Georgia http:// www.economy.ge/?page=news&nw=1042d/ |Last visit 07.05.2019|;
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) INCLUSIVE GROWTH https//|www.oecd.org/inclusive-growth/#introduction/ [Last visit 07.05.2019];
- United Nations Development Programme 2015. What Does Inclusive Economic Growth Actually Means in Practise. https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/blog/2015/7/31/What-does-inclusive-economic-growth-actually-mean-in-practice-.html/ |Last visit 07.05.2019|;
- World Economic Forum. The Global Competitiveness Report 2017–2018. 201 27 September. P. 124-125;
- WORLD INEQUALITY REPORT 2018. World Inequality Lab. P. 8; https://wir2018.wid.world/files/download/wir 2018-summary-english.pdf Last visit 07.05.2019|









